In modern telecommunications, data transmission is a complex technologies to ensure high-speed, reliable communication through long distances. PDH (Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy), SONET (Synchronous Optical Network), and SDH (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy) are important in transmitting digital data.
What are differences between PDH vs SONET vs SDH? Through this article, we can understand what PDH, SONET, SDH is and what the Differences are between PDH, SONET and SDH.
What is PDH?
PDH (Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy), is an early digital transmission standard to handle the transport of digital signals over copper and fiber-optic networks. It appeared in the 1980s and developed rapidly.
PDH, in the form of traditional point-to-point connection of various media. Although it is high precision, but difficult to achieve strict global synchronisation, so it is called ‘almost-synchronous’.
What is SDH?
SDH, Synchronous Digital Hierarchy, is also a digital transmission standard. it defines as a multiplex technology used in the telecommunication.
With the changing needs of communications, SDH originated from the Bell Communications Research Institute's Synchronous Optical Networking (SONET). SDH aimed to meet the challenges of large-scale fiber optic transmission. It can facilitate seamless integration of products from different manufacturers.
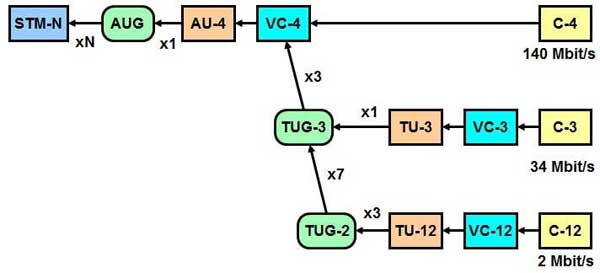
SDH Work principal
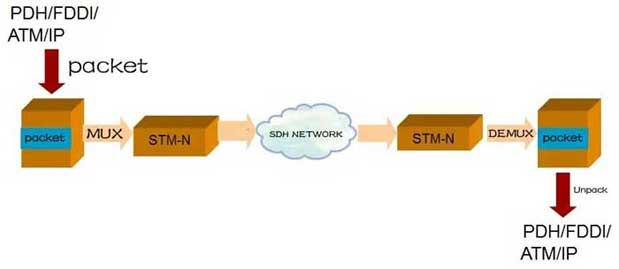
Signals from other systems serve as payloads and are packaged into appropriate STM-N signals for transmission in the SDH network. Go to the other end to unpack, take out the payload, and restore the original signal.
SDH connection: SDH can be connected with other devices either point-to-point or in a ring link or star-link.
What is SONET?
In 1985, Bellcore proposed the SONET (Synchronous Optical Network) standard, and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) adopted a series of standards for SONET. It has become a common technical system suitable for optical fiber.
SONET (Synchronous Optical Network) is a standardized digital communication protocol used in optical fiber networks to transmit large amounts of data over long distances.
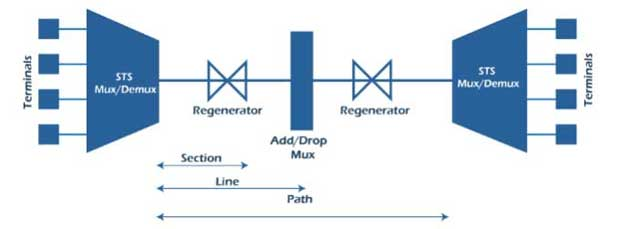
Working principal
What are differences between PDH vs SONET vs SDH?
Feature
|
PDH
|
SONET
|
SDH
|
Synchronization
|
Plesiochronous
|
Synchronous
|
Synchronous
|
Geographical Usage
|
Europe
|
North America
|
Worldwide (mainly Europe, Asia)
|
Application
|
Point-to-point link(Only equipment from the same manufacturer)
|
Ring link(One or more manufacturers' equipment)
|
Ring link(One or more manufacturers' equipment)
|
Data Rates
|
Lower rates (E1, E3, T1, T3)
|
High rates (STS-1, STS-3, STS-48)
|
High rates (STM-1, STM-64)
|
Multiplexing
|
Less efficient
|
More efficient, standardized
|
More efficient, standardized
|
Frame Structure
|
Non-standardized
|
Fixed and standardized frame
|
Fixed and standardized frame
|
Network Management
|
Less advanced
|
Advanced, with APS and protection
|
Advanced, with APS and protection
|
Interoperability
|
Limited between PDH levels
|
High interoperability in North America
|
High interoperability globally
|
Synchronization:
PDH: PDH is "plesiochronous," This lack of exact synchronization can lead to inefficiencies in managing data rates and timing.
SONET: SONET is "synchronous," meaning that it uses a common clock for all the signals within the network, ensuring precise synchronization. This makes it more efficient and easier to manage than PDH.
SDH: SDH is also "synchronous," just like SONET, but it is based on a different clocking and structure. It is the European counterpart to SONET and is designed to work internationally. SDH allows for both synchronous and asynchronous transfer. In contrast, the SONET may only send data in synchronous mode.
Application:
PDH: PDH is in the form of traditional point-to-point connection of various media. Different brands of PDH fiber equipment can not work to each other. It is the main limitations of PDH.
Both using Baudcom PDH is available.
Using Baudcom PDH and other brands PDH is unavailable, they can not be compatible.

SDH and SONET: They can be connected either point-to-point or in a ring link or star-link, and different brands device can be connected to each other. Unified bit rate and interface standards for efficient interconnection between devices.
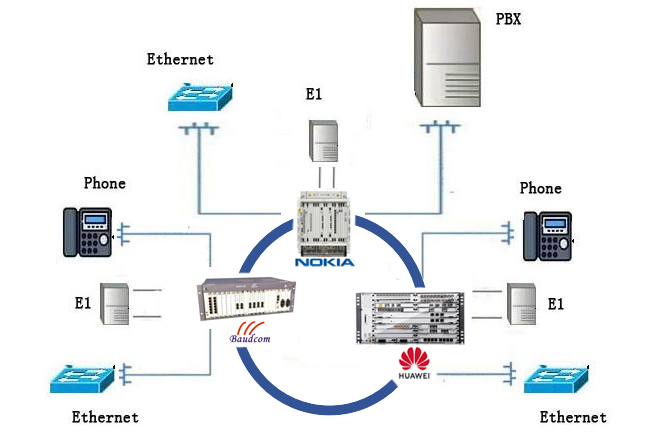
Architecture:
PDH: PDH is an older technology primarily used for transporting voice and low-speed data over copper or fiber optic links, which makes it less efficient compared to SONET and SDH.
SONET : SONET is a fiber-optic-based technology that provides a standardized optical transmission system. It uses a hierarchical, time-division multiplexing (TDM) system where each signal is synchronized with the others.
SDH: SDH provides a similar hierarchical multiplexing structure to SONET but is more adaptable to different regional and international standards. It uses an optical transmission system and allows for the integration of different types of data streams (voice, video, data).
Data Rates:
PDH: PDH supports lower data rates compared to SONET and SDH. The basic rates in PDH systems: E1 (Europe): 2.048 Mbps; E3 (Europe): 34.368 Mbps; T1 (USA): 1.544 Mbps; T3 (USA): 45 Mbps.
SONET: SONET supports much higher data rates compared to PDH. Key SONET rates include: OC-1: 51.84 Mbps; OC-3: 155.52 Mbps; OC-12: 622.08 Mbps; OC-48: 2.488 Gbps; OC-192: 9.953 Gbps.
SDH: SDH uses different multiplexing levels, and its rates are often aligned with SONET rates but defined in terms of the STM (Synchronous Transport Module) levels. Key SDH rates include: STM-1: 155.52 Mbps; STM-4: 622.08 Mbps; STM-16: 2.488 Gbps; STM-64: 9.953 Gbps. Due to the absence of high-order multiplexing for signal transfer, SONET proffers lower transmission rates than SDH.
Application Area:
PDH: PDH is primarily used in legacy systems and is more common in Europe.
SONET: SONET is mainly used in North America and parts of Japan.
SDH: SDH is primarily used in Europe and other regions that follow International Telecommunication Union standards.
Fault Tolerance:
PDH: PDH does not have sophisticated mechanisms for automatic fault detection or recovery.
SONET: SONET has fault detection, providing high reliability and network resiliency. This is the same as SDH.
Cost:
PDH device cost is low much than SONET or SDH device. For example, 16E1 fiber multiplexer, the 16E1 PDH fiber multiplexer cost is only half of the 16E1 SDH terminal device.
If the project is small and it is point to point application, the best choice is PDH device. If your application need ring application and different brands compatiblity, you need to choose the SONET or SDH fiber optical equipment.
Related article:
SDH vs PDH | Difference between PDH and SDH