OLT vs Switch: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to networking equipment, terms like OLT and Switch are frequently used, but many people may not understand the difference between the two. Both serve important roles in managing data traffic, but they are used in different contexts and for different purposes. In this blog post, we’ll explore what each device is, how they function, and how they differ from each other.
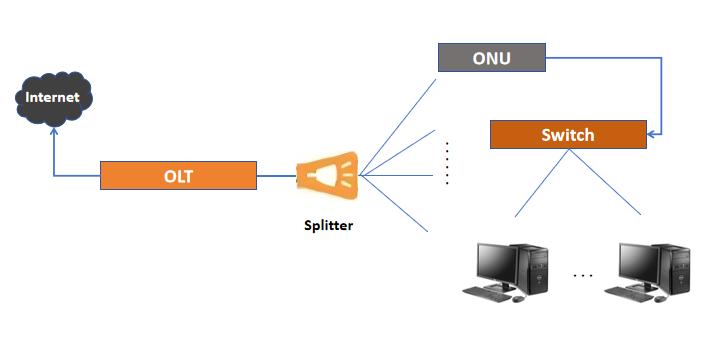
What is an OLT (Optical Line Terminal)?
An Optical Line Terminal (OLT) is a crucial piece of equipment in Fiber to the Home (FTTH) networks, commonly found in Passive Optical Networks (PONs). It acts as the central point of control and connection between the fiber-optic network and the broader telecommunications infrastructure.
Key Functions of OLT(Optical Line Terminal):
1. Connection Point to the Core Network: The OLT serves as the interface between the service provider’s core network and the optical distribution network (ODN).
2. Traffic Aggregation: It aggregates data from multiple Optical Network Units (ONUs) or Optical Network Terminals (ONTs), which are located at the end users' premises.
3. Bandwidth Management: The OLT manages bandwidth allocation to ensure efficient use of the optical fiber. It assigns bandwidth dynamically to individual users and manages traffic quality.
4. Data Communication: It transmits downstream data to ONUs/ONTs and collects upstream data, ensuring seamless communication.
Learn more about: Basic Knowledge About OLT
In short, the OLT is a core device that manages and connects fiber-optic networks to the rest of the internet infrastructure.

What is a Switch?
A network switch, on the other hand, is a device used in a local area network (LAN) to connect different devices, like computers, servers, printers, and other network devices, within the same network. Switches can be used in both wired and wireless optical switch network, depending on the setup.

Key Functions of a Switch:
1. Data Forwarding: Switches are responsible for forwarding data packets between devices within the same optical switch network. They work by learning the MAC addresses of devices on the network and forwarding data only to the device it is intended for.
2. Network Segmentation: A switch divides a network into smaller segments, allowing better management of traffic and reducing congestion.
3. Support for Multiple Devices: Switches can support multiple ports, allowing many devices to communicate with each other simultaneously.
4. Performance Enhancement: Because switches operate at Layer 2 (Data Link layer) of the OSI model, they help optimize optical switch network performance by reducing collisions and improving efficiency compared to older hubs.
Switches are often used in office environments or within data centers, connecting all the devices in a specific local area.
Key Differences Between OLT and Switch
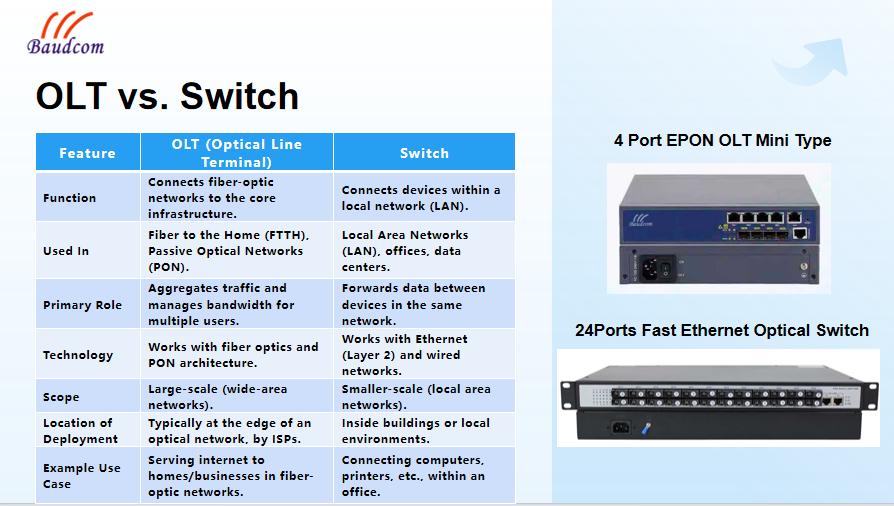
1. Functionality:
OLT: The OLT manages and connects optical networks to core infrastructure, often in fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) environments. It’s a central management device in a passive optical network.
Switch: A switch connects devices within a local area network (LAN), directing data between computers, printers, servers, and other devices within the same network.
2. Deployment Location:
OLT: Typically deployed by internet service providers at the edge of a fiber-optic network to serve residential or business customers.
Switch: Used inside homes, businesses, or data centers to interconnect devices in a local network.
3. Network Scope:
OLT: OLTs are used for wide-area networks (WANs), typically to manage fiber-optic traffic over large distances and across many users.
Switch: Switches manage traffic within a smaller, local network, usually within a single building or a limited geographic area.
4. Technology:
OLT: Operates in the optical network layer and works with fiber optics, managing upstream and downstream data in a PON setup.
Switch: Operates in the Ethernet layer, typically handling wired data and packet switching at a much smaller scale.
5. Use Case:
OLT: Essential for internet service providers offering fiber-optic broadband services. It is central to FTTH/FTTP (Fiber to the Premises) architectures.
Switch: Used in almost any LAN environment to interconnect devices and create efficient, reliable networks.
Conclusion: OLT vs Switch – Which One Do You Need?
In summary, OLT and Switch are both fundamental networking devices, but they serve different purposes. The OLT is an essential part of a fiber-optic network infrastructure, providing connectivity and traffic management for large-scale, high-speed internet services. A switch, on the other hand, is used for efficient data communication within smaller, local networks, such as within an office or home.
Understanding the distinction between these two devices helps you appreciate the different layers of networking, whether it’s the backbone of a wide-area network or the internal workings of a local network.