GEPON(EPON) and GPON are popular versions of
passive optical networks (PONs). These short-haul networks of fiber-optical
cable are used for Internet access, voice over Internet protocol (VoIP), and
digital TV delivery in metropolitan areas. The primary differences between them
lie in the protocols used for downstream and upstream communications.
GPON:
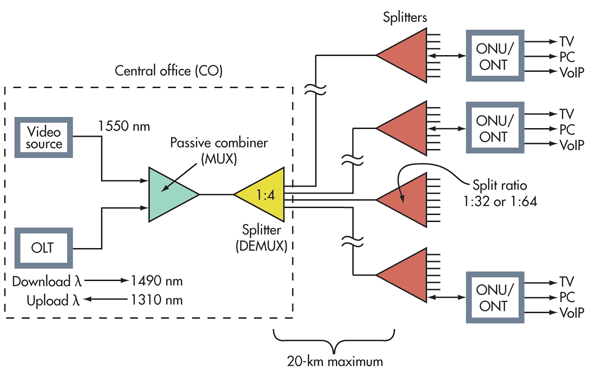
GPON (Gigabit PON) is the evolution of broadband PON (BPON) standard. The
protocols used by GPON are ATM, GEM, and Ethernet. GPON uses optical wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) so a single fiber
can be used for both downstream and upstream data. A laser on a wavelength (λ)
of 1490 nm transmits downstream data. Upstream data transmits on a wavelength
of 1310 nm. If TV is being distributed, a wavelength of 1550 nm is used.It supports higher rates and has more security.
GEPON:
GEPON or EPON (Ethernet PON) is
an IEEE standard that uses Ethernet for sending data packets. PON is fully compatible with other Ethernet standards,
so no conversion or encapsulation is necessary when connecting to
Ethernet-based networks on either end. GEPON
uses 1 gigabit per second upstream and downstream rates. In current there are
15 million EPON ports installed.
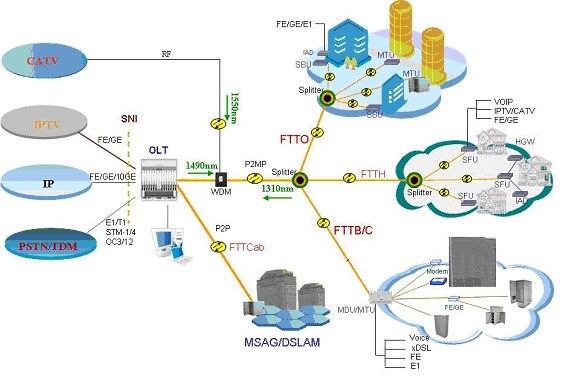
EPON/GEPON is a fast Ethernet over passive optical networks which are
point to multipoint to the premises (FTTP) or fiber to the home (FTTH)
architecture in which single optical fiber is used to serve multiple premises
or users.
The Differences between GEPON and GPON:
The differences that make the GEPON the best are discussed here.
One important distinction between the standards is operational speed. BPON
is relatively low speed with 155 Mbps upstream/622 Mbps downstream operation.
GE-PON/EPON operates at 2.5 Gbps symmetrical operation. GPON supports 1 Gbps
asymmetrical operation. Another key distinction is the protocol support for
transport of data packets between access network equipment.
BPON is based on ATM, GPON uses native Ethernet and GEPON supports
ATM, Ethernet and WDM using a superset multi-protocol layer.
GEPON is still evolving; but, it requires the multiple protocols through
translation to support the native Generic Encapsulation Method (GEM) transport
layer. This emulation supports ATM, Ethernet and WDM protocols. It is widely
deployed in Asia and uses Ethernet as its
native protocol and simplifies timing and lowers the costs by using symmetrical
2.5 Gbps data streams. The complexity is lower and cost is less than GPON.
GEPON has an installation cost advantage.
GEPON Supports Class of Service (CoS) operation for time-sensitive
transport of data payloads such as video. This video frames must be delivered
in sequence and it should maintain time constraint to prevent malfunction. It
functions with VoIP.
When compared to GPON, GEPON is highly scalable and flexible; it provides
service for more than 2,300 subscribers. It is used in telecommunication
services. GEPON supports effective education and public outreach (EPO). This
network will: It provides
infrastructure to facilitate collaboration between scientists, educators etc.Provides
support systems for professional development.
ADVANTAGES OF GEPON:
There are many advantages of the GEPON. They are listed and discussed here.
- Service flexibility: The GEPON does lots of services and it is of very
flexible type.
- Easy, modular planning and rollout: The GEPON is the easiest mechanism and
there is modular planning and roll out that is attached with the GEPON which
adds lots of benefits to the GEPON differentiating from the GPON.
- Highest density and availability.
- Price. GEPON solutions at the time of writing are more cost effective
- Much more easy configuration - easier to use, almost plug and play technology.
BAUDCOM is profesional communication equipement manufacture, which has majored in FTTH more than ten years. BAUDCOM can provide both GPON an EPON FTTX solution.
More PON production information
BAUDCOM GPON OLT
BAUDCOM GPON ONT
BAUDCOM EPON OLT
BAUDCOM EPON ONU