What is Optical Amplifier?
An optical amplifier, also
called an erbium-doped fiber amplifier or erbium amplifier, abbreviated as EDFA,
is an optical or IR (Infrared Radiation) repeater that amplifies a modulated
laser beam directly, without opto-electronic and electro-optical conversion.
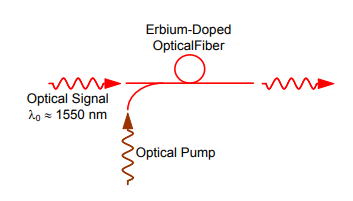
The device uses a short length of optical fiber doped with the rare-earth
element erbium. When the signal-carrying laser beams pass through this fiber,
external energy is applied, usually at IR wavelengths. This so-called pumping
excites the atoms in the erbium-doped section of optical fiber, increasing the
intensity of the laser beams passing through. The beams emerging from the EDFA
retain all of their original modulation characteristics, but are brighter than
the input beams.
An erbium-doped fiber
amplifier
Amplifier
Types
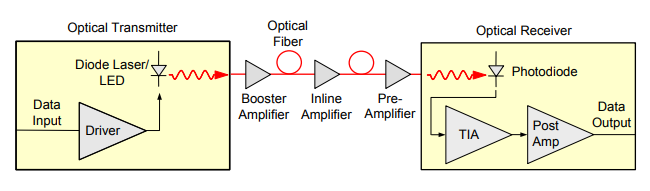
There are three major
applications for optical fiber amplifiers: booster amplifier, in-line
amplifier, and pre-amplifier. These applications are described in more details
below:
Booster
Amplifier
Booster amplifiers are
placed directly after the optical transmitter. In this application, booster
amplifier is adopted to compensate for the losses of optical elements between
the laser and optical fibers so that the increased transmitter power can be used
to go further in the link.
In-line
Amplifier
In-line amplifiers or
in-line repeaters are placed along the transmission link to compensate for the
losses incurred during propagation of optical signal. They take a small input
signal and boost it for re-transmission down the fiber. Here it should also be
pointed out that to control the signal performance and the noise added by the EDFA is important, because noise added by amplifier will limit the system
length.
Pre-Amplifier
Pre-amplifiers are placed
just before the receiver to increase the signal level before the photo
detection takes place in an ultra-long haul system so as to improve receiver
sensitivity. By placing a pre-amplifier, a much larger signal can be presented
to the receiver, thus easing the demands of the receiver design.
Optical amplifiers in a
fiber optic data link
What is Light Surge?
The large power signal light, which has a pulse
shape of a high energy, is called a light surge, and may cause damage in
optical elements constituting the optical amplifier and devices connected along
the signal output line.
How to prevent Occurrence of Light Surge?
The use of EDFA makes the input optical power
increase rapidly. However, because the dynamic gain of EDFA changes slowly, an
optical surge will be generated at the moment of the energy jump of the input
signal. This surge is the instantaneous increase of the output optical power
and a sharp peak, especially when the EDFA is cascaded; the optical surge
phenomenon is more obvious. The peak optical power can reach several watts.
Such a high optical power is likely to cause damage to the photoelectric
converter and optical connector.
The method to solve the optical surge is to
realize the automatic optical power reduction (APR) or automatic optical power
shutdown (APSD) function in the EDFA, that is, the EDFA automatically reduces
the power or automatically shuts off the power when there is no input light,
thereby suppressing the surge phenomenon happened.
Baudcom’s EDFA has a slow-start function, which can effectively reduce
optical surges and effectively protect EDFA equipment and other equipment on
related optical links. The slow start function makes the EDFA and other optical
device in fiber link work more stable and longer product life.
Here is a short video showing slow-start protection function of EDFA:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=48h27JxVz0I

Built-in WDM 8Ports High Power EDFA
Baudcom offers several
kinds of optical amplifiers (EDFA). For more information, please visit Baudcom.