Single-mode Fiber vs. Multimode Fiber
Single Mode Fiber
Single mode fiber is a fiber featuring a small light-carrying core of
about 9 micrometers (μm) in diameter. For reference, a human hair is closer to
100 μm. The core is surrounded by a cladding that brings the overall diameter
of the optical fiber to 125 μm. Single-mode fiber cable has only one mode of
propagation: a single wavelength of light in the fiber core. This means there’s
no interference or overlap between the different wavelengths of light to garble
your data over long distances like there is with multimode cable.
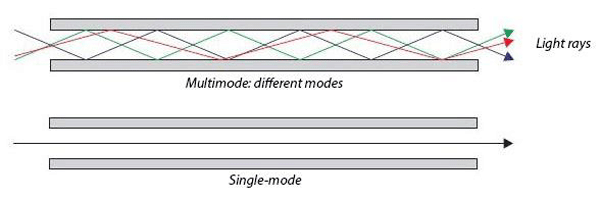
Multimode Fiber
Multimode fiber is a fiber with a core of 50 μm
or above. A larger core means multiple modes (or rays of light) can travel down
the core simultaneously. Just like single mode, the core is surrounded by a
cladding that brings the overall diameter of the optical fiber to 125 μm.
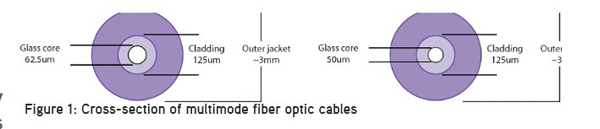
What are 50μm fiber and 62.5μm fiber?
The numbers 50μm and 62.5μm refer to the diameters of the glass or
plastic core, the part of the fiber that carries the light which encodes your
data. The dimensions are sometimes specified as 50/125μm and 62.5/125μm, to
include the diameter of the cladding. (The cladding confines the light to the
core because it has a lower index of refraction.) Cable construction is shown
in the following diagram, indicating the cable core, cladding, and outer jacket
diameters.
The Difference
Although the 50-micron fiber has a smaller core, which is the
light-carrying part of the fiber, the glass cladding diameter of the 62.5 and
50-micron cables is the same, both being 125 microns. You can use both cables
in the same type of network, but it is recommended to use 50-micron cables for
local applications: backbone, horizontal, and internal building connections,
and special consideration should be given to any new buildings and
installations. Both types can use LED or laser light sources. The main difference
between 50-micron and 62.5-micron cables is that the bandwidth of 50-micron
cables is three times that of standard 62.5-micron cables, especially at 850
nanometers. As lasers are increasingly used as light sources, the 850-nanometer
wavelength becomes more and more important. Other differences are distance and
speed. 50-micron cables provide longer link lengths and/or higher speeds at 850
nm wavelength.
Which One Should I Choose?
With the
increasing demand for network capacity, upgrade plans must focus on the future.
The installation of 50μm multimode fiber today brings the direct benefits of
longer cable distances and improved optical loss budget margins, and prepares
for future network upgrades. If you haven't started yet, now is the time to
start phasing out 62.5μm fiber and move to the world 50μm for higher
performance.
Baudcom offers a variety of fiber optic cables. For more information about fiber optic cables,
please visit Baudcom.