INFORMATION
Overview
Session Border Controller is the boundary gate of IP voice network, it’s mainly used to solve voice conversation traversal during network address translation, provide secure communication supporting and voice quality assurance.
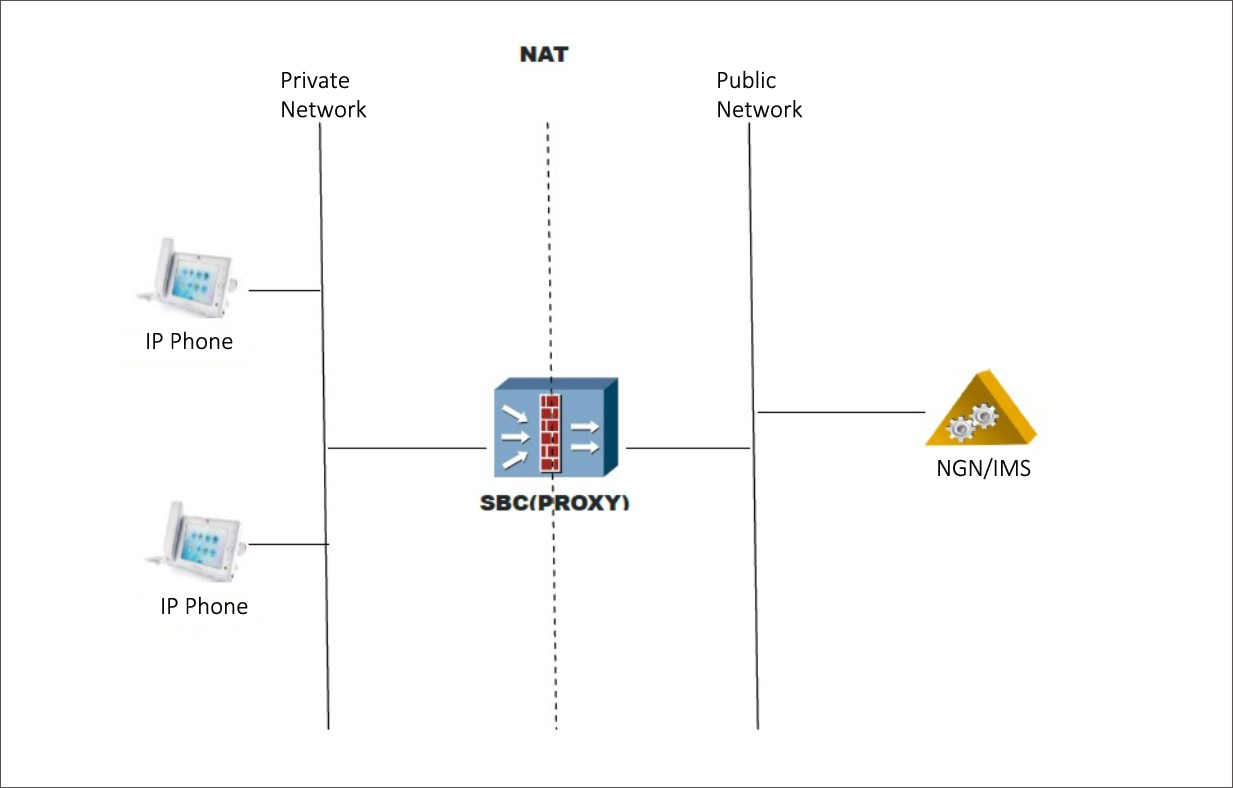
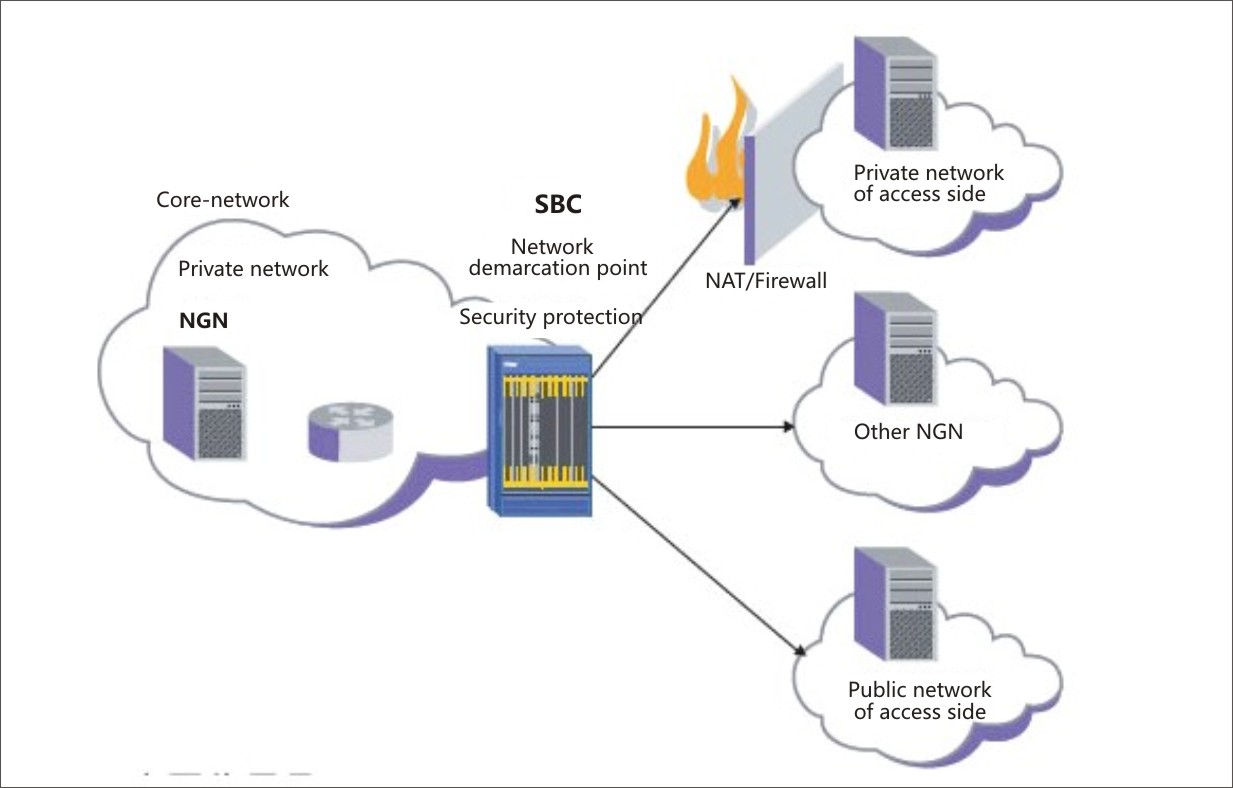
Session Border Controller is deployed in the edge of VOIP service provider network (between soft switch platform and voice access gateway), or in the outlet of enterprise VPN network.
It controlled and processed call signaling across IP network and talk burst in real-time. Session Border Controller is also support to develop IP service.
SBC carries out the real-time communication requirement of IP voice interconnection, such as access control, firewall traversal, voice compression restoring, signaling interworking, information security assurance (encryption and decryption), illegal access intercepting, management QOS (Quality of Service)etc.
What is SBC?
A session border controller (SBC) is a device regularly deployed in Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) networks to exert control over the signaling and usually also the media streams involved in setting up, conducting, and tearing down telephone calls or other interactive media communications.
Early deployments of SBCs were focused on the borders between two service provider networks in a peering environment. This role has now expanded to include significant deployments between a service provider's access network and a backbone network to provide service to residential and/or enterprise customers.
The term "session" refers to a communication between two parties – in the context of telephony, this would be a call. Each call consists of one or more call signaling message exchanges that control the call, and one or more call media streams which carry the call's audio, video, or other data along with information of call statistics and quality. Together, these streams make up a session. It is the job of a session border controller to exert influence over the data flows of sessions.
The term "border" refers to a point of demarcation between one part of a network and another. As a simple example, at the edge of a corporate network, a firewall demarcates the local network (inside the corporation) from the rest of the Internet (outside the corporation). A more complex example is that of a large corporation where different departments have security needs for each location and perhaps for each kind of data. In this case, filtering routers or other network elements are used to control the flow of data streams. It is the job of a session border controller to assist policy administrators in managing the flow of session data across these borders.
The term "controller" refers to the influence that session border controllers have on the data streams that comprise sessions, as they traverse borders between one part of a network and another. Additionally, session border controllers often provide measurement, access control, and data conversion facilities for the calls they control.
Functions
1. Signaling encryption: support multiple form of encryption like TLS/SRTP, encrypt/decrypt signaling.
2. Voice proxy: forward RTP packet of talk burst, traversal of NAT/Firewall.
3. Video proxy: support video transportation protocol H.263/H.264, transmission of RTP packet of video media stream, and traversal of NAT/Firewall.
4. Voice Compression: restore scathe less compression, continue to compress voice in the G.729, save bandwidth.
5. Security Policy: filtrate voice steam/signaling steam, intercept illegal IP packet, hide NAT address, prevent hostile attack, encrypt/decrypt voice steam, signaling and security log information, prevent forwarding MGCP message of conflicting account.
6. Certification/Registration: support the registration and certification of gateway.
7. Standard Protocol: support IMS, SIP, SIP-T, RTP/RTCP, TLS, SRTP, HTTP, and TCP/UDP.
8. Work mode: SIP registration and SIP trunk.
9. QOS Guarantee: provide voice quality (packet loss rate, jitter, time delay) monitoring, guarantee call quality;
Higher priority to routing service (flow control), limit concurrent calls, provide calling and called information, distinguish media steam etc.
10. Network Error Monitoring: network default diagnoses.
Status Accounting: monitor and count up online gateway information,concurrent calls and call duration etc.
Performance
Here are two models: BD-SE160 and BD-SE1000. BD-SE160 has 1 pcs of mother board, BD-SE1000 has 8 pcs of mother board.
Performance for per mother board, is as same as performance of BD-SE160, performance of BD-SE1000 is eight times of mother board & BD-SE160.
1. Maximum Concurrent Calls:
Under SIP registration mode, BD-SE160 has 1000 concurrent calls; BD-SE1000 has 8000 concurrent calls;
Under SIP trunk mode, BD-SE160 has 8000 concurrent calls; BD-SE1000 has 8000 concurrent calls;
2. Maximum SIP users:
Under SIP registration, BD-SE160 has 10000 SIP users; BD-SE1000 has 80000 SIP users.
3. Packet Delay: less than 30 microseconds.
Note: if there are large-scale concurrent video calls, the maximum concurrent calls will be determined by the bandwidth that occupied by video. For example, the bandwidth occupied by video is 1M bps, one channel of video is equivalent to ten channels of voice, then model BD-SE160 can support up to 50 concurrent video calls, BD-SE1000 can support up to 500 concurrent video calls.
Management
1. User interface: Web GUI page.
2. Maintenance and Administration: Support RS232 serial interface / Telnet / remote.
3. Configuration and maintenance.
Specification
Name/Model
|
BD-SE160
|
BD-SE1000
|
Slot for
Mother Board
|
1
|
8
|
Ethernet Interface
|
4 10/100/1000M Base-T
|
4 10/100/1000M Base-T
|
Serial Interface
|
1 RS232(CONSOLE PORT)
|
1 RS232(CONSOLE PORT)
|
Power Modules
|
DC-48V or AC110-240V
|
DC-48V or AC110-240V
|
Power
|
40W
|
150W
|
Dimension
|
472mm*325mm*44mm (1U)
|
472mm*260mm*154mm (3.5U)
|
Weight
|
4.5KG
|
8KG
|
Environment
|
0℃-50℃ less than 80%
|
0℃-50℃ less than 80%
|
Application Topology:
Ordering information
Related Products